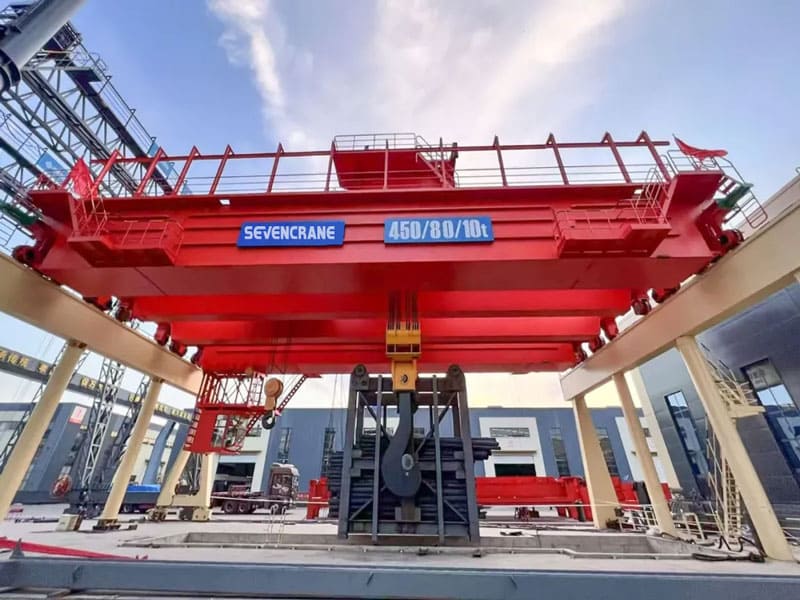
Smart cranes are revolutionizing the lifting industry by integrating advanced safety technologies that greatly reduce operational risks and enhance workplace safety. These intelligent systems are designed to monitor, control, and respond to real-time conditions, ensuring safe and efficient crane operations.
1. Overload Protection via Weight Sensing
Smart cranes are equipped with load sensors that continuously monitor the weight being lifted. When the load approaches or exceeds the crane’s rated capacity, the system automatically prevents further lifting, avoiding structural damage or tipping accidents.
2. Anti-Collision with Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric detection devices help prevent collisions by sensing nearby objects. This feature is crucial in crowded or confined working environments, helping to avoid damage to equipment, structures, and personnel.
3. Power-Off Braking System
In the event of an unexpected power outage, the crane’s braking system automatically activates to securely hold the load in place. This ensures that materials do not fall, preventing dangerous accidents.
4. Intelligent Monitoring and Early Warning
Smart monitoring systems continuously check the operational status of the crane. If any irregularities are detected—such as overheating, abnormal vibrations, or electrical faults—visual and audible alarms are triggered to alert operators in real time.
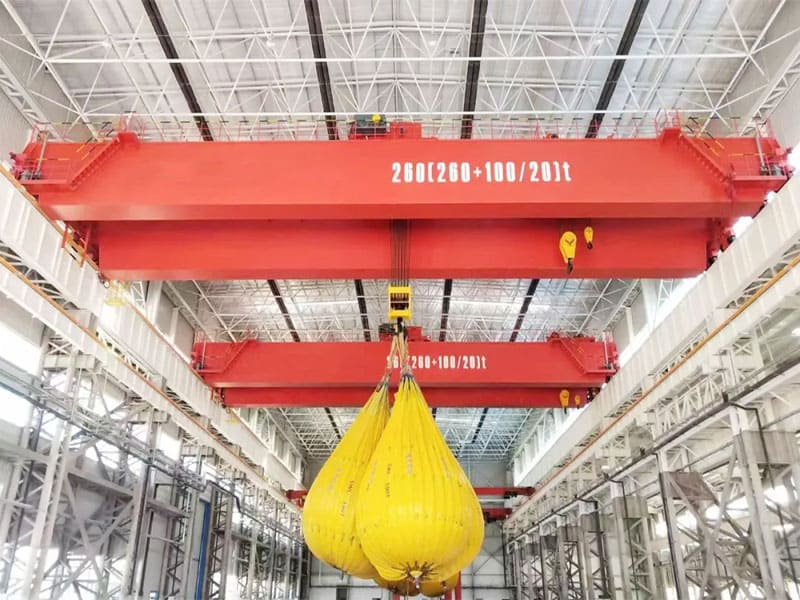


5. Load Stabilization System
To reduce swinging or tipping during lifting, smart cranes include load stabilization mechanisms. These systems maintain load balance even under dynamic conditions, providing safer transport of materials.
6. Auto Stop at Ground Contact
Once the lifted load reaches the ground, the system can automatically stop lowering. This prevents the hook or cable from going slack, which could otherwise damage the crane or injure personnel.
7. Precision Positioning
Smart cranes offer fine motion control that enables centimeter-level positioning. This accuracy is especially beneficial for placing loads in exact locations, such as during equipment installation or tight warehouse stacking.
8. Fault Diagnosis and Safety Control
Self-diagnostic systems detect internal faults and automatically initiate safety protocols, directing the crane into a safe state to prevent hazards.
9. Remote Operation and Monitoring
Operators can control and observe crane operations from a safe distance, minimizing direct exposure to hazardous zones.
Together, these integrated safety features make smart cranes a highly secure solution for modern lifting operations.
Post time: Apr-15-2025